Vertebral Compression Surgeon in Kolkata
Overview
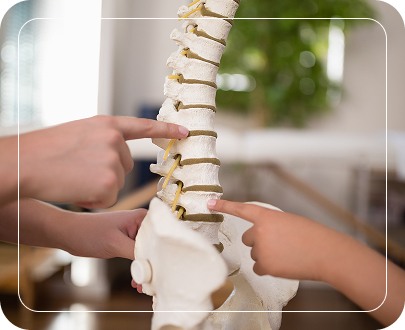
Types of Vertebral Compression
-
Wedge Fractures:
The front part of the vertebra breaks and collapses.
-
Crush Fractures:
The entire vertebra breaks under pressure.
-
Burst Fractures:
The vertebra breaks in multiple directions.
-
Acute Vertebral Compression Fracture:
Sudden collapse of a vertebra due to trauma or weakened bones.
-
Chronic Compression Fracture:
Gradual loss of vertebral height over time, usually due to osteoporosis.
-
Pathologic Compression Fracture:
Caused by cancerous tumours weakening the vertebrae.
-
Lumbar 1 Compression Fracture:
A specific fracture at the L1 vertebra, affecting lower back stability and movement.
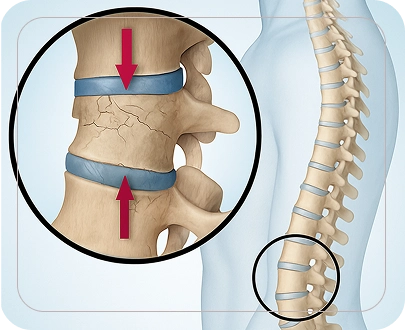
Signs that you need a Vertebral Compression Surgery
Discuss your condition with Dr. Rohit Mishra for vertebrae compression treatment if you experience:



Height loss

Height loss
Curved spine (kyphosis) or hunched posture/dowager’s hump
Curved spine (kyphosis) or hunched posture/dowager’s hump

Difficulty in daily activities

Difficulty in daily activities
Limited spine movement

Limited spine movement

Spine stiffness

Spine stiffness

Sharp pain feeling more than weeks

Sharp pain feeling more than weeks

Numbness or tingling in severe cases

Numbness or tingling in severe cases

Difficulty in breathing

Difficulty in breathing

Increased risk of future fractures

Increased risk of future fractures
Book an appointment today
Causes & Risk Factors of Vertebral Compression
- Osteoporosis (weakened bones)
- Trauma from falls or accidents
- Bone cancers (e.g., multiple myeloma)
- Spinal infections
- Age-related bone degeneration
- Heavy lifting or spinal overloading
- Long-term steroid use
- Poor bone health and nutrition
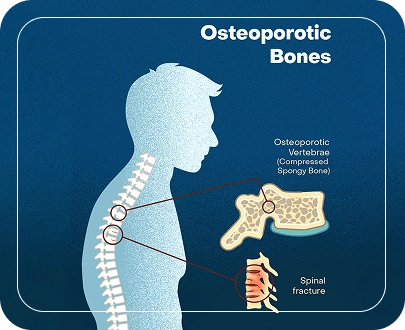
Diagnosis of Vertebral Compression

Physical examination

Physical examination

Bone density test

Bone density test

CT scans

CT scans

X-rays


MRI Scans

MRI Scans
Vertebrae Compression Treatment
Non-surgical
- Pain management
- Bracing
- Physical therapy
- Medication
- Rest and activity modification
- Nerve root blocks
- Epidural injections
Surgical
- Vertebroplasty/Balloon kyphoplasty
- Kyphoplasty
- Spinal fusion
- Decompression surgery
FAQs
Can vertebral compression fractures heal on their own?
Is vertebroplasty a major surgery?
Is vertebroplasty painful?
Vertebroplasty treatment is generally well-tolerated, and doctors immediately relieve pain. Before the surgery, consult with Dr. Mishra to discuss your concerns.
How can I prevent vertebral compression fractures?
What activities should I avoid with a spinal compression fracture?
Avoid heavy lifting, bending forward, twisting movements and high-impact activities. Your doctor will provide specific guidelines based on your condition.